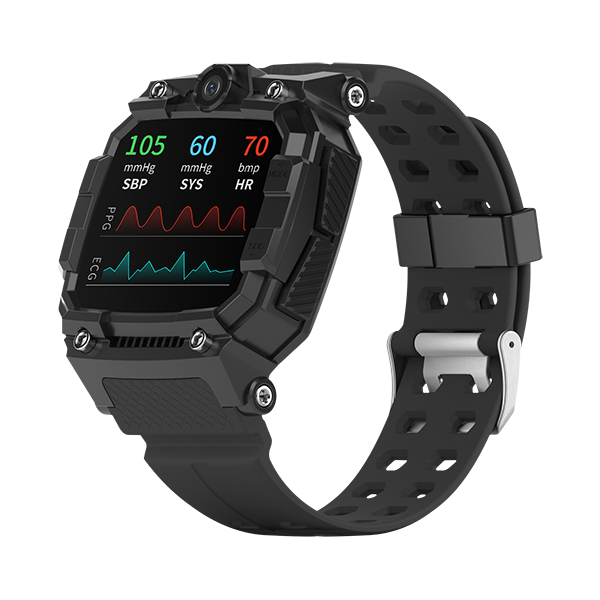
Geo Fence Principle Explanation
How does the Geo fence work?
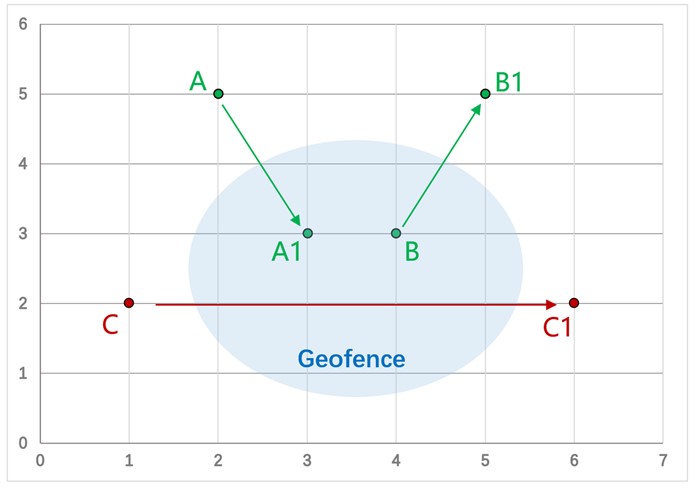
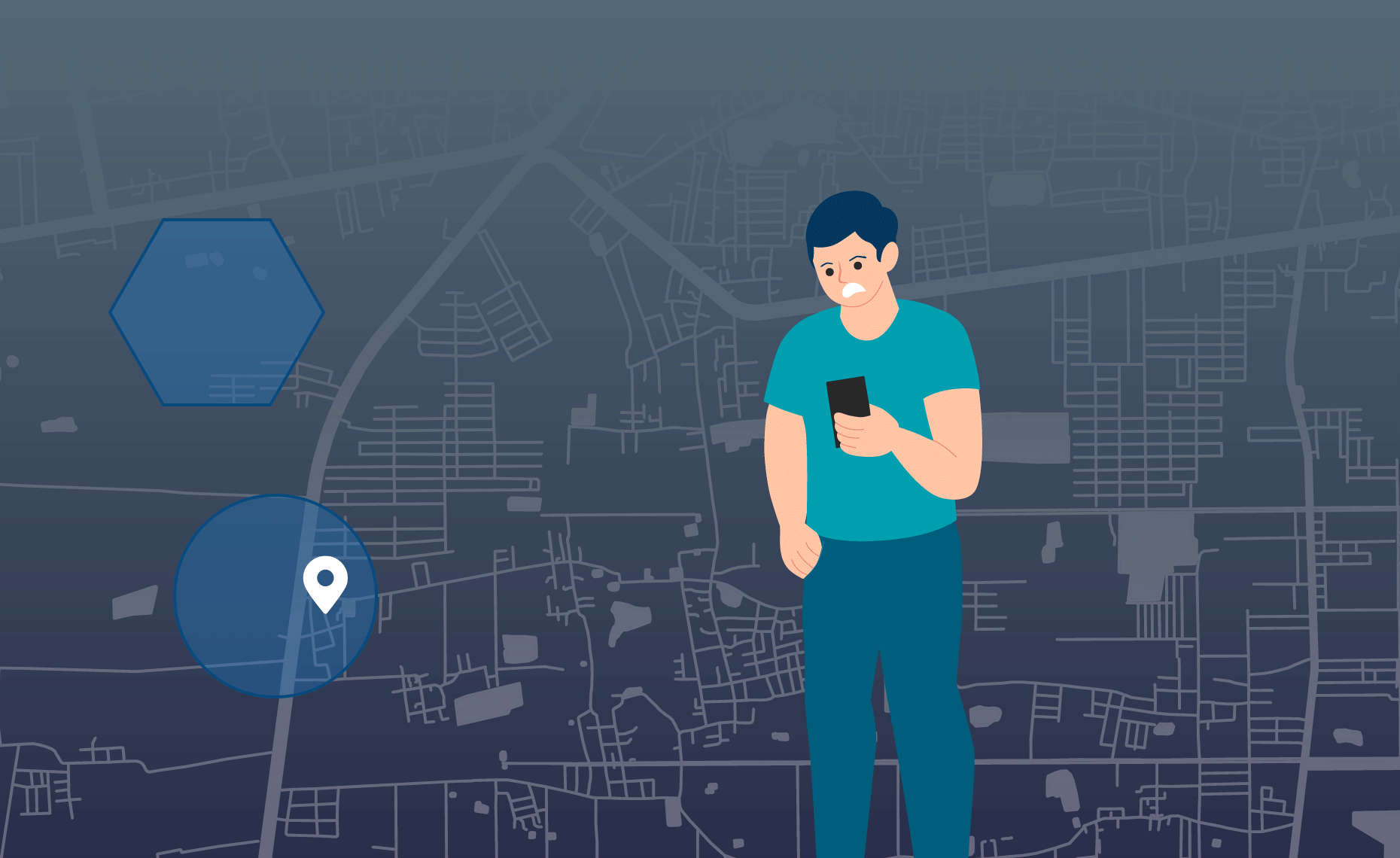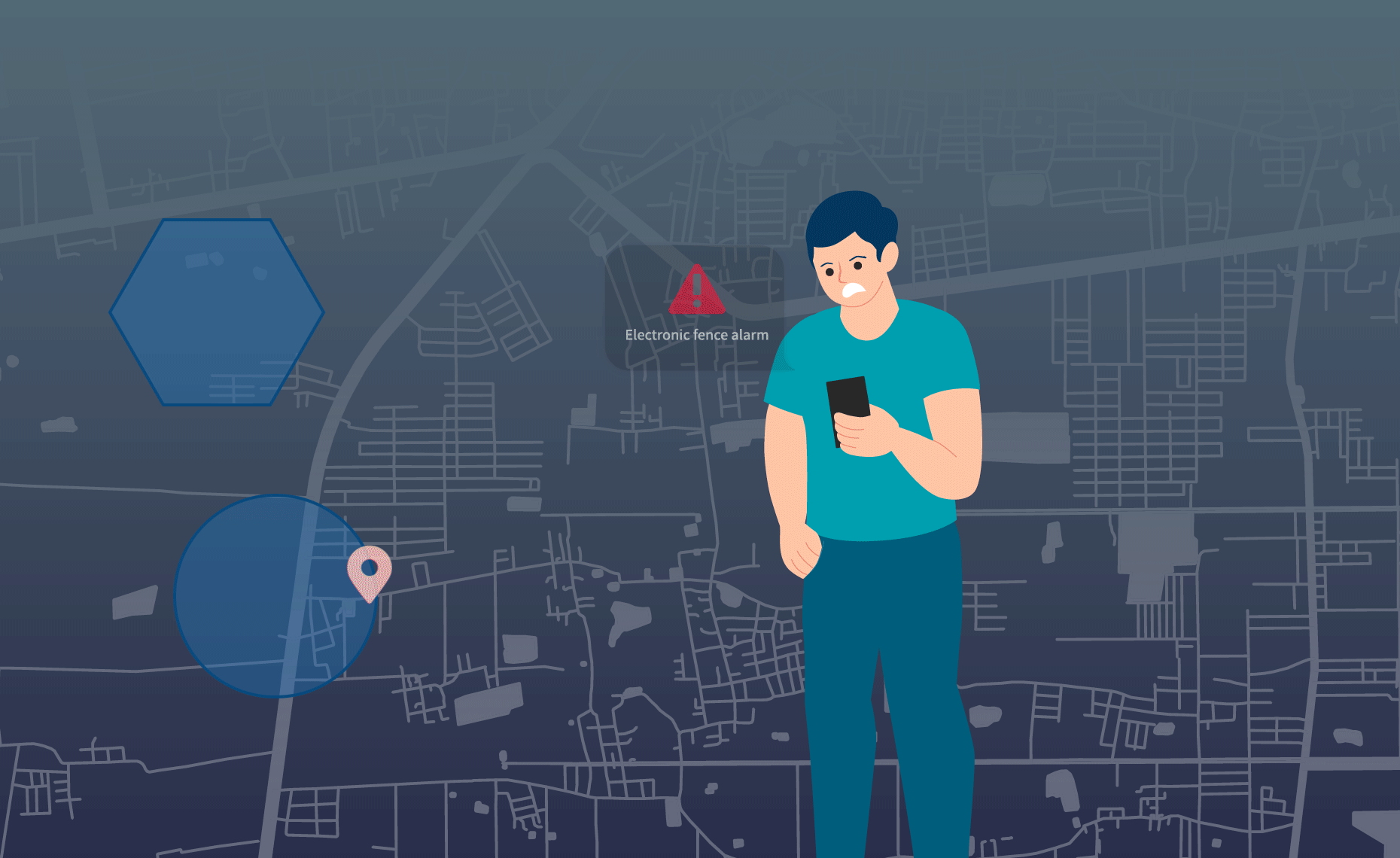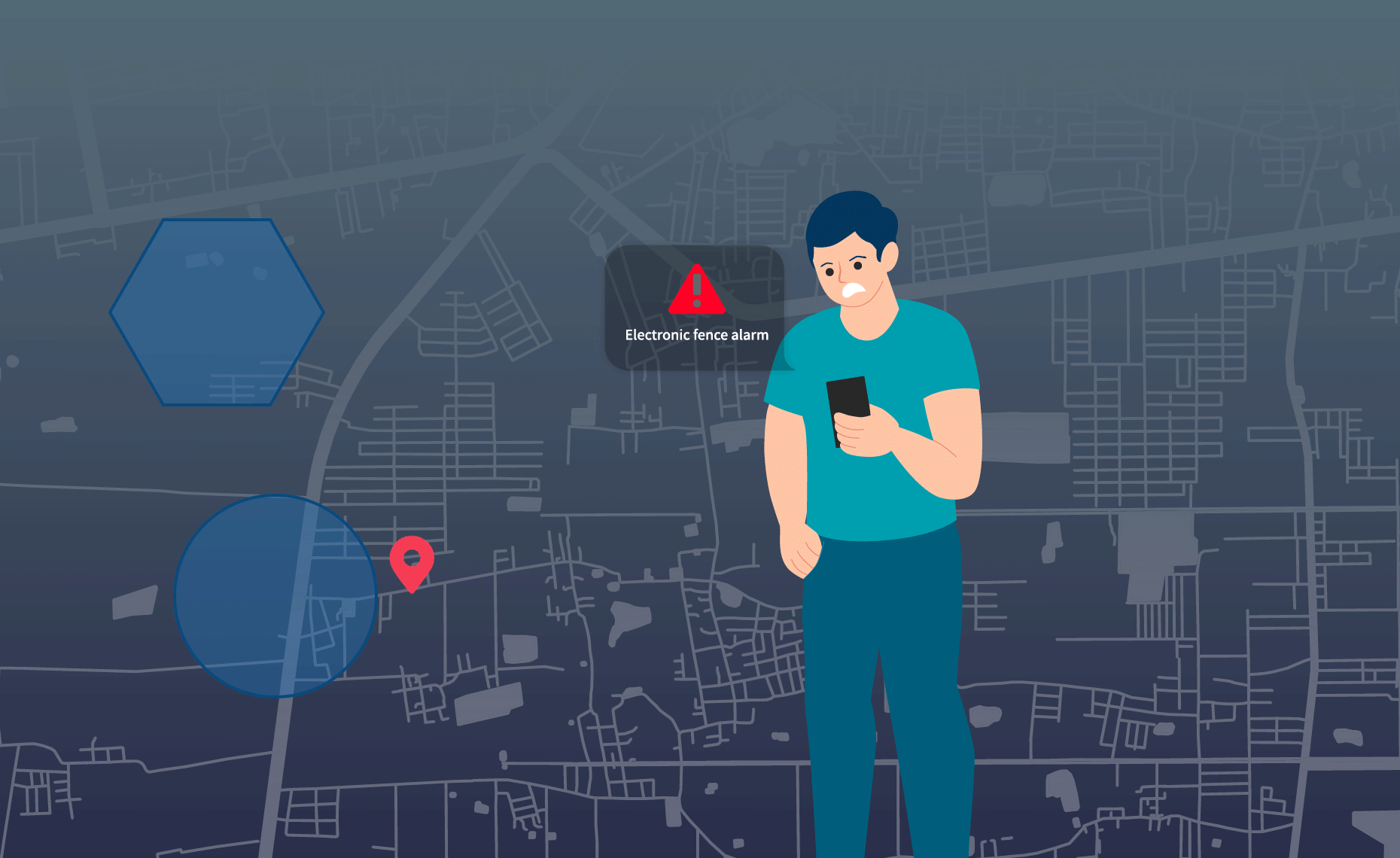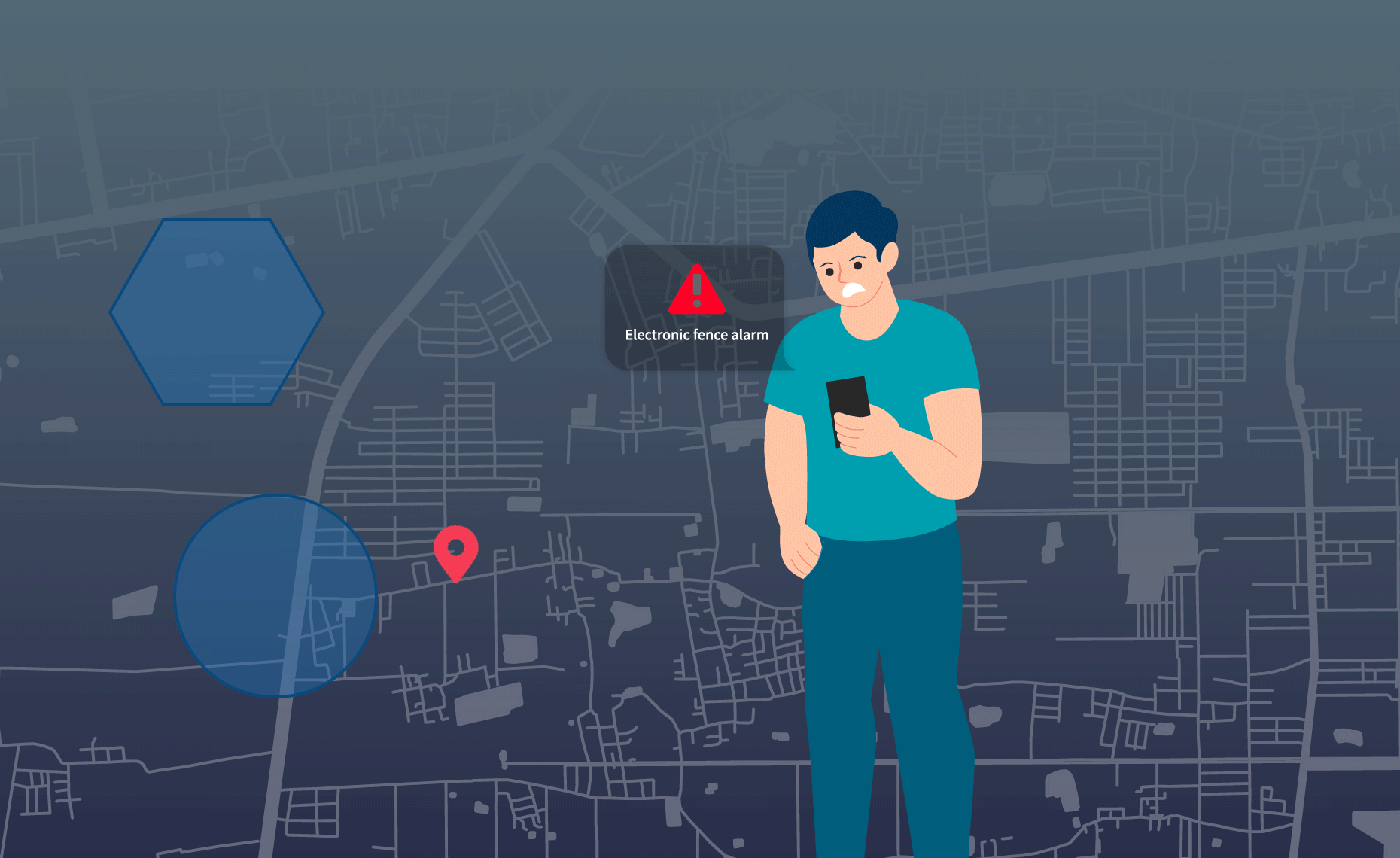
As shown in the figure, the administrator pre-defines a series of coordinate data on the server to delineate the scope of the Geo fence.
The positioning device regularly reports its location data to the server, which includes coordinate data and positioning time. The server compares the adjacent two sets of location data with the electronic fence range and infers whether the device has entered or left the fence based on the comparison results:
- If the previous location data (A) is outside the fence and the subsequent data (A1) is inside the fence, an “entry into the fence alarm” will be triggered.
- If the previous location data (B) is inside the fence and the subsequent data(B1) is outside the fence, a “fence exit alarm” will be triggered.
- If both sets of data are inside or outside the fence, no alarm will be triggered.
How are false alarms/missed alarms/delayed alarms generated?
If the time interval for the device to upload location data is long, or if the device enters a building, tunnel, valley, or between high-rise buildings causing positioning failure, the distance between adjacent location data may be significant. The device may have actually crossed the Geo fence range, but the server receives two adjacent sets of location data that both fall outside the fence range, resulting in no alarm being triggered and causing a missed alarm.
As shown in the figure above, the coordinates C and C1 are both outside the fence. Therefore, no fence alarm will be triggered. In reality, the device crossed the fence range between the two data points, but the server, based only on C and C1, cannot determine the device’s actual movement path, resulting in a missed alarm.
Is the electronic fence a function of the device end or the server end?
The electronic fence is a server-side software function. The data processing occurs on the server side and does not require computation on the device end. The location data processed by the electronic fence comes from the device. As long as the device regularly reports its location data to the server, the server can implement the Geo fence function.
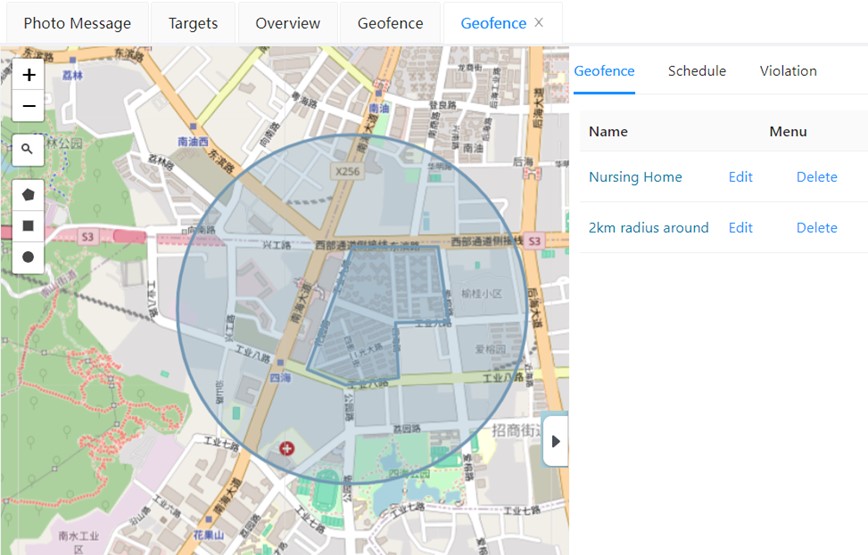
Does positioning accuracy affect the accuracy rate of fence alarms? How to improve alarm accuracy?
Yes. Each positioning method is influenced by various factors, resulting in different positioning accuracies. Due to insufficient positioning accuracy, the location data reported by the device may be far from its actual location, which may cause the server to generate missed alarms, false alarms, or delayed alarms. Additionally, if the device uploads location data at a large time interval (e.g., every 30 minutes), the accuracy rate of electronic fence alarms will also be reduced. Considering that increasing positioning frequency usually leads to higher power consumption, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the actual usage scenarios of the wearer and the device’s battery capacity to set an appropriate positioning frequency.
Tracking with BLE Beacon
Moreover, when the device is in a building, tunnel, valley, mine, or narrow street between high-rise buildings, GPS signals may be blocked, causing positioning failure. If the positioning accuracy obtained through Wi-Fi positioning is also insufficient in such cases, Bluetooth beacons can be considered for auxiliary positioning.
Thinkrace has developed GPS tracker and high precision positioning functions based on Bluetooth beacons. Please contact us for more information.
Click here for demo video of indoor Geo fence: https://youtu.be/T7jTPjwW5Ec